About CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA (CCA)
What is cholangiocarcinoma?
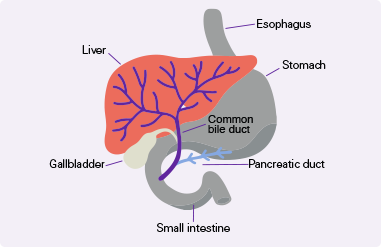
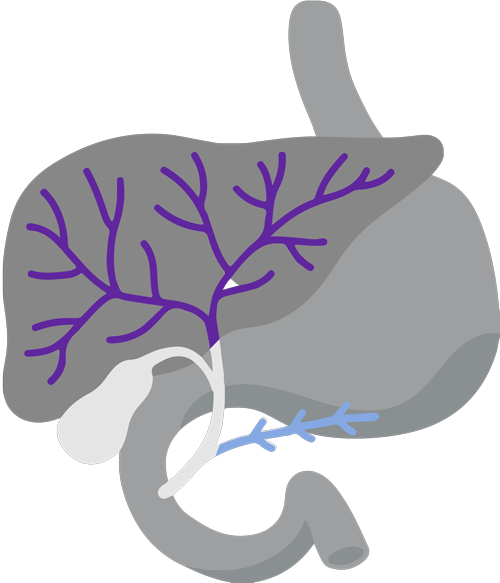
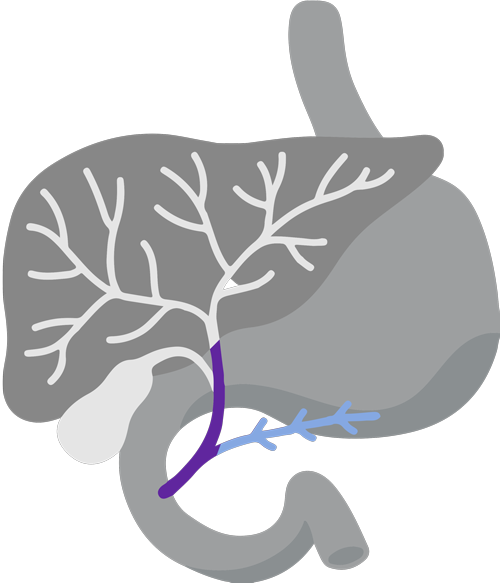
Digestive system diagram showing the bile duct.
CholangiocarcinomaCholangiocarcinoma, also called bile duct cancer, is a rare cancer that forms in the bile ducts., also called Bile ducts are tubes that carry bile (fluid made by the liver) between the liver and gallbladder and the small intestine.bile duct cancer, is a rare and aggressive cancer that forms in the bile ducts inside and around the liver. It accounts for about 3% of cancers in the gastrointestinal systemGastrointestinal system includes the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. It also includes the salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, which help the body digest food and liquids. Also called the digestive system..
Approximately 8000 people in the United States are diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma each year, but because it is a difficult cancer to diagnose, the actual number of cases may be higher.
Signs and symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma are not specific, and many cases are not diagnosed until the disease has progressed when surgery may no longer be an option. The recommended treatment will depend on whether or not the tumor has advanced or metastasizedAdvanced cholangiocarcinoma means there are several tumors in the bile ducts. Metastatic cholangiocarcinoma means the cancer has spread to other places in the body, such as nearby tissue, lymph nodes, or more distant parts of the body..

Digestive system diagram showing the bile duct.
Types of cholangiocarcinoma
According to the site of origin:
According to the tumor location:
- If the tumor stays in the place it first formed, it is called localized disease
- If there are several tumors in the bile ducts or if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, it is called advanced or metastatic disease. If it has spread to other places in the body, such as a lung, it is still considered to be cholangiocarcinoma
Genetic mutations in cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma can develop because of certain genetic abnormalities, or mutationsMutations are changes in the DNA sequences of cells. Mutations may be caused by mistakes during cell division, or they may be caused by exposure to DNA-damaging agents in the environment. Certain mutations may lead to cancer or other diseases.. Genetic mutations are changes in the DNA of a cell. They can result in cells growing and dividing without the usual controls. Over time, a mass of uncontrolled cells can grow and become a tumor.
Biomarker testing
Your doctor may recommend biomarker testingBiomarker testing involves a piece of tumor (from biopsy or surgery) being sent to
the laboratory for analysis to check for certain genes, proteins, or other molecules that may be a sign of a disease or condition, such as cancer. to look for specific changes in the DNA of the cancer cells.
Biomarker testing involves a piece of your tumor (obtained from biopsy or surgery) being sent to the laboratory for analysis.
It may take a few weeks to get results, but the results will enable your doctor to personalize the best approach to treating your type of cancer.
HOW TREATMENT WITH TIBSOVO WORKS
Targeting IDH1 mutations in cholangiocarcinoma
The first treatment of its kind, TIBSOVO is a targeted therapyTargeted therapy is a type of treatment that can block the action of certain molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells with less harm to normal cells. that works against the IDH1IDH1 stands for isocitrate dehydrogenase-1. In healthy cells, IDH1 plays an important role in normal chemical reactions. When IDH1 is altered due to a genetic mutation, it may promote the development of certain types of cancers, including cholangiocarcinoma. mutation. IDH1 stands for isocitrate dehydrogenase-1. In healthy cells, the IDH1 gene makes the IDH1 protein, which plays a role in normal chemical reactions within cells. When the IDH1 gene is altered due to a genetic mutation, cells make an abnormal (mutated) version of the IDH1 protein. This mutated IDH1 protein may promote the development of certain types of cancers, including cholangiocarcinoma.
Up to 20% of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomaIntrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma means the tumor originates in the bile ducts inside the liver. cases have an IDH1 mutation. That's why biomarker testing for mutations can help your healthcare team understand if TIBSOVO is right for you.
How TIBSOVO works against your cholangiocarcinoma
Targeted Therapy
TIBSOVO specifically targets the mutated IDH1 protein, which can
slow down the progression of advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
TIBSOVO works differently from traditional chemotherapyChemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cells that divide quickly, including cancer cells and cells in healthy tissue.. Chemotherapy kills cells that divide quickly, including both tumor cells and cells in healthy tissue. Chemotherapy is also typically given by infusionInfusion therapy is when medication or fluids are administered through a needle or catheter. Also called intravenous infusion, it's a way of delivering medication that can't be taken orally or that needs to be dispensed at a controlled pace., which usually takes place in an infusion center.
Proven results
For patients with advanced mutated IDH1 cholangiocarcinoma who
have been previously treated, targeted therapy with TIBSOVO has been shown to increase the length of
time a person can live with cholangiocarcinoma without the disease getting worse.
Convenient once-daily pill
TIBSOVO is a pill that's typically prescribed for
patients to take 2 tablets once a day. You can take TIBSOVO at home with or without food and without the infusion time requirements of chemotherapy.
Traditional chemotherapy is cytotoxicCytotoxic means toxic to living cells, “cyto” means cell and “toxic” means poison, as in chemotherapy drugs that kill cancer cells., which means it kills both abnormal and healthy cells. Unlike chemotherapy, TIBSOVO only targets tumor cells with mutated IDH1.